 Just like animals, there are nutrients which are essential to plant survival. Three major macronutrients have been identified which are essential to plant survival: nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. In fertilizers and other applications, these nutrients can be abbreviated as NPK. Each of these essential nutrients is associated with a different function within the plant: nitrogen is for leaf growth, phosphorus is essential for the roots, and potassium assists in flowering and forming fruits. The NPK ratio is printed on fertilizer bags. Fertilizers in which the ratio of each is about the same is a general-purpose fertilizer. However, the nutrient concentrations may vary based on the intended use of the fertilizer. For example, different levels of NPK would be found in fertilizer for fruits than in fertilizer for grasses. Most fertilizers also contain smaller concentrations of other, less vital nutrients. Some examples of nutrients of lesser importance include sulfur, magnesium, zinc, and iron. If you were to fertilize a garden of fruits and vegetables, you should always choose to use a fertilizer high in phosphorus. Phosphorus is important in fruit development, and using such fertilizer produces larger and better-tasting fruits.
Just like animals, there are nutrients which are essential to plant survival. Three major macronutrients have been identified which are essential to plant survival: nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. In fertilizers and other applications, these nutrients can be abbreviated as NPK. Each of these essential nutrients is associated with a different function within the plant: nitrogen is for leaf growth, phosphorus is essential for the roots, and potassium assists in flowering and forming fruits. The NPK ratio is printed on fertilizer bags. Fertilizers in which the ratio of each is about the same is a general-purpose fertilizer. However, the nutrient concentrations may vary based on the intended use of the fertilizer. For example, different levels of NPK would be found in fertilizer for fruits than in fertilizer for grasses. Most fertilizers also contain smaller concentrations of other, less vital nutrients. Some examples of nutrients of lesser importance include sulfur, magnesium, zinc, and iron. If you were to fertilize a garden of fruits and vegetables, you should always choose to use a fertilizer high in phosphorus. Phosphorus is important in fruit development, and using such fertilizer produces larger and better-tasting fruits.
Monday, November 21, 2016
Plant Nutrition
 Just like animals, there are nutrients which are essential to plant survival. Three major macronutrients have been identified which are essential to plant survival: nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. In fertilizers and other applications, these nutrients can be abbreviated as NPK. Each of these essential nutrients is associated with a different function within the plant: nitrogen is for leaf growth, phosphorus is essential for the roots, and potassium assists in flowering and forming fruits. The NPK ratio is printed on fertilizer bags. Fertilizers in which the ratio of each is about the same is a general-purpose fertilizer. However, the nutrient concentrations may vary based on the intended use of the fertilizer. For example, different levels of NPK would be found in fertilizer for fruits than in fertilizer for grasses. Most fertilizers also contain smaller concentrations of other, less vital nutrients. Some examples of nutrients of lesser importance include sulfur, magnesium, zinc, and iron. If you were to fertilize a garden of fruits and vegetables, you should always choose to use a fertilizer high in phosphorus. Phosphorus is important in fruit development, and using such fertilizer produces larger and better-tasting fruits.
Just like animals, there are nutrients which are essential to plant survival. Three major macronutrients have been identified which are essential to plant survival: nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. In fertilizers and other applications, these nutrients can be abbreviated as NPK. Each of these essential nutrients is associated with a different function within the plant: nitrogen is for leaf growth, phosphorus is essential for the roots, and potassium assists in flowering and forming fruits. The NPK ratio is printed on fertilizer bags. Fertilizers in which the ratio of each is about the same is a general-purpose fertilizer. However, the nutrient concentrations may vary based on the intended use of the fertilizer. For example, different levels of NPK would be found in fertilizer for fruits than in fertilizer for grasses. Most fertilizers also contain smaller concentrations of other, less vital nutrients. Some examples of nutrients of lesser importance include sulfur, magnesium, zinc, and iron. If you were to fertilize a garden of fruits and vegetables, you should always choose to use a fertilizer high in phosphorus. Phosphorus is important in fruit development, and using such fertilizer produces larger and better-tasting fruits.
Monday, November 14, 2016
Road Salt Makes Frogs Male
 Salt is commonly used on northern streets to de-ice roads. Studies have shown that tadpole populations that have been exposed to salt have a 10% lower female population. This study suggests that more frogs turn out as males as a result of being exposed to salt. This was likely due to a sex-reversing mechanism, in which the sodium ion from a sodium chloride molecule could bind to a receptor and act in the place of testosterone. In addition to causing fewer females in the population, the resulting females are smaller than average, possibly hindering their ability to produce eggs. This shift in population toward males combined with the accompanying problematic females could put entire populations of frogs at risk. This research could have implications for other species in sex ratios as well as other traits.
Salt is commonly used on northern streets to de-ice roads. Studies have shown that tadpole populations that have been exposed to salt have a 10% lower female population. This study suggests that more frogs turn out as males as a result of being exposed to salt. This was likely due to a sex-reversing mechanism, in which the sodium ion from a sodium chloride molecule could bind to a receptor and act in the place of testosterone. In addition to causing fewer females in the population, the resulting females are smaller than average, possibly hindering their ability to produce eggs. This shift in population toward males combined with the accompanying problematic females could put entire populations of frogs at risk. This research could have implications for other species in sex ratios as well as other traits.
Monday, November 7, 2016
Kinetic Labyrinth: Rotational Motion
The kinetic labyrinth functions via the semicircular
canals. There are three semicircular
canals all at right angles to one another.
The function of the kinetic labyrinth is to detect if the body is in rotational motion. Detection happens in the
ampulla, which spans the canal. Inside
the ampulla lies the crista ampullaris.
It is made up of cupula and contains hair cells. Furthermore, it is attached to sensory nerve
fibers. Endolymph fills the canals and
is caused to move upon acceleration of the body. This movement is detected by the
ampulla. The information gathered is
sent to the vestibular nuclei, somatosensory cortex, spine, and cerebellum in
order to be processed and translated into information regarding balance,
position, posture, and movement.
Sunday, November 6, 2016
The Static Labyrinth: Linear Acceleration
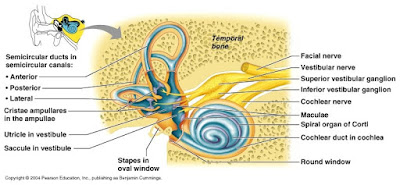 The static labyrinth evaluates head position shift or acceleration and deceleration and translates that into data about the position of your body. In the vestibule, you will find the utricle and saccule. Within the utricle and saccule, you will find the maculae, which are the sensory structures. There, there are hair cells nestled within support cells. On top of the hair cells, there is stereocilia and kinocilia. On top of that are otoliths within the gelatinous otolithic matrix. This matrix shifts based on the position of the head. Movement of the matrix is detected by hair cells. Displacement of the stereocilia in the direction toward the tallest stereocilia causes depolarization of the afferents. Displacement of the stereocilia toward the shortest stereocilia causes hyperpolarization of the afferents. The vestibular nuclei coordinate spinal posture. The somatosensory cortex processes the information gathered by the static labyrinth. Signals are sent to the cerebellum and relay as muscle movements in the head and eyes.
The static labyrinth evaluates head position shift or acceleration and deceleration and translates that into data about the position of your body. In the vestibule, you will find the utricle and saccule. Within the utricle and saccule, you will find the maculae, which are the sensory structures. There, there are hair cells nestled within support cells. On top of the hair cells, there is stereocilia and kinocilia. On top of that are otoliths within the gelatinous otolithic matrix. This matrix shifts based on the position of the head. Movement of the matrix is detected by hair cells. Displacement of the stereocilia in the direction toward the tallest stereocilia causes depolarization of the afferents. Displacement of the stereocilia toward the shortest stereocilia causes hyperpolarization of the afferents. The vestibular nuclei coordinate spinal posture. The somatosensory cortex processes the information gathered by the static labyrinth. Signals are sent to the cerebellum and relay as muscle movements in the head and eyes.
Saturday, November 5, 2016
Sound Transduction in Human Ears
 Sound travels down the external auditory meatus and vibrates
the tympanic membrane. The vibration
passes to the malleus, incus, and then the stapes. The sound then enters the oval window and
travels into the bony labyrinth. It
causes vibrations of the perilymph inside the scala vestibuli. Some sound enters the membranous labyrinth by
vibrating the vestibular membrane. This
causes vibrations of the endolymph, which vibrates the basilar and tectorial
membranes. These membranes clap
together. Between the membranes lies the
organ of corti. The organ of corti
creates graded potentials in response to the vibrations of the basilar and
tectorial membranes via specialized structures known as hair cells. The vibration then can pass through the scala
tympani, through the round window, and into the mouth via the auditory tube.
Sound travels down the external auditory meatus and vibrates
the tympanic membrane. The vibration
passes to the malleus, incus, and then the stapes. The sound then enters the oval window and
travels into the bony labyrinth. It
causes vibrations of the perilymph inside the scala vestibuli. Some sound enters the membranous labyrinth by
vibrating the vestibular membrane. This
causes vibrations of the endolymph, which vibrates the basilar and tectorial
membranes. These membranes clap
together. Between the membranes lies the
organ of corti. The organ of corti
creates graded potentials in response to the vibrations of the basilar and
tectorial membranes via specialized structures known as hair cells. The vibration then can pass through the scala
tympani, through the round window, and into the mouth via the auditory tube.Thursday, November 3, 2016
Emmetropia: Normal Vision
 In emmetropia, or normal vision, the center of the visual
field is in sharp focus, and the periphery is blurred. The retina on the nasal side of each eye is
responsible for the peripheral vision on that side. The retina on the temporal side is
responsible for the overlapping field on the opposing side of the body. Light hitting the fovea gives the sharpest
image right in the center of the field of view.
Once light strikes the retina, photoreceptors generate graded potentials
and pass them to the optic nerve. Peripheral
vision has to cross the body in the optic chiasm because of the brain’s
contralateral processing. The
information is carried to the thalamus, which routes the information to the
optic radiations. From there, it travels
to the occipital lobe for processing.
Light that fell on the optic disc generates no image.
In emmetropia, or normal vision, the center of the visual
field is in sharp focus, and the periphery is blurred. The retina on the nasal side of each eye is
responsible for the peripheral vision on that side. The retina on the temporal side is
responsible for the overlapping field on the opposing side of the body. Light hitting the fovea gives the sharpest
image right in the center of the field of view.
Once light strikes the retina, photoreceptors generate graded potentials
and pass them to the optic nerve. Peripheral
vision has to cross the body in the optic chiasm because of the brain’s
contralateral processing. The
information is carried to the thalamus, which routes the information to the
optic radiations. From there, it travels
to the occipital lobe for processing.
Light that fell on the optic disc generates no image.Tuesday, November 1, 2016
Neurology Exam
On Wednesday, November 8, 2016, the world will know who the next president of the United States will be. However, more importantly, I have a neurology exam. The exam will cover the senses: smell, taste, vision, hearing, and somatosensations. I have just begun to review material for the exam. You should expect the next few posts to be related to the material that will be on the exam. If you happen to be in a neurology class, perhaps the posts will serve as a bit of a helpful review for you as well.
Continue Reading...
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Designed By Templateism | Seo Blogger Templates


